
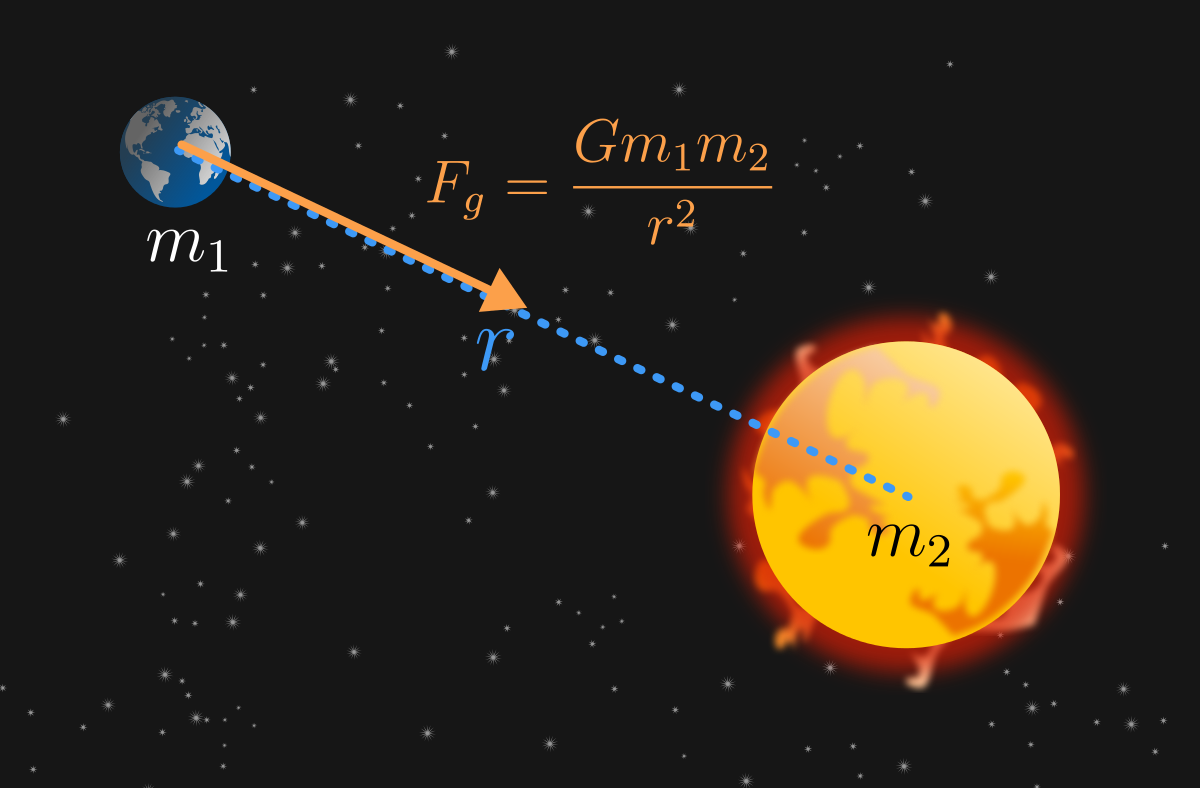
The gravitational attraction between any two objects is therefore given by one of the most famous equations in all of science:į gravity = G M 1 M 2 R 2 F gravity = G M 1 M 2 R 2 The more mass an object has, the stronger the pull of its gravitational force. Newton also concluded that the gravitational attraction between two bodies must be proportional to their masses. Put the planet three times farther away, and the force is ( 1 3 ) 2 ( 1 3 ) 2, or 1 9 1 9 as large. In other words, if a planet were twice as far from the Sun, the force would be ( 1 2 ) 2 ( 1 2 ) 2, or 1 4 1 4 as large. Eventually he was able to conclude that the magnitude of the force of gravity must decrease with increasing distance between the Sun and a planet (or between any two objects) in proportion to the inverse square of their separation. The answer to this question required mathematical tools that had not yet been developed, but this did not deter Isaac Newton, who invented what we today call calculus to deal with this problem. How must the force of gravity depend on distance in order for these conditions to be met? Also, that gravitational force had to predict the correct behavior of falling bodies on Earth, as observed by Galileo. The precise mathematical description of that gravitational force had to dictate that the planets move exactly as Kepler had described them to (as expressed in Kepler’s three laws). Once Newton boldly hypothesized that there was a universal attraction among all bodies everywhere in space, he had to determine the exact nature of the attraction. (This may seem part of our everyday thinking today, but it was a remarkable insight in Newton’s time.) If so, the attractive force between the Sun and each of the planets could keep them in their orbits. He further hypothesized that gravity is not limited to Earth, but that there is a general force of attraction between all material bodies. Newton’s insight was that Earth’s gravity might extend as far as the Moon and produce the force required to curve the Moon’s path from a straight line and keep it in its orbit.
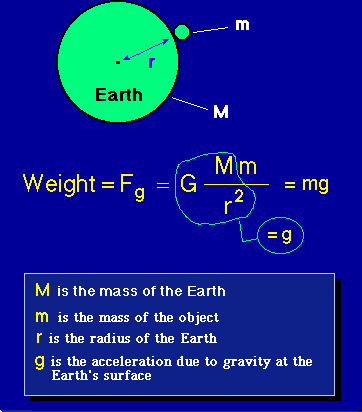
If you drop something, it accelerates toward Earth as it falls. Everyday experience shows us that Earth exerts a gravitational force upon objects at its surface. In Newton’s time, gravity was something associated with Earth alone.
That force, Newton proposed, was gravity. But the planets move in ellipses, not straight lines therefore, some force must be bending their paths. Thus, it is the straight line that defines the most natural state of motion. Newton’s laws of motion show that objects at rest will stay at rest and those in motion will continue moving uniformly in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. Describe how Newton’s universal law of gravitation extends our understanding of Kepler’s laws.Explain what determines the strength of gravity.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
